Atmosphere
An introduction to Atmosphere
Name: Own Teacher
Email: info@ownteacher.com
Created At: 01-11-2023
The Earth's Atmosphere:
The Earth's atmosphere is a layer of gases that envelops the planet. It's essential for life as we know it and plays a crucial role in various Earth processes. The atmosphere consists of a mixture of gases, each with distinct properties. Here's a full explanation of the atmosphere, along with its classification:
Composition:
- The atmosphere primarily consists of:
- Nitrogen (N2): About 78% of the atmosphere.
- Oxygen (O2): Approximately 21%.
- Argon (Ar): Roughly 0.93%.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2): Approximately 0.04%.
- Trace Gases: Including neon, helium, methane, and more.
- Water Vapor (H2O): Variable, but typically around 1%.
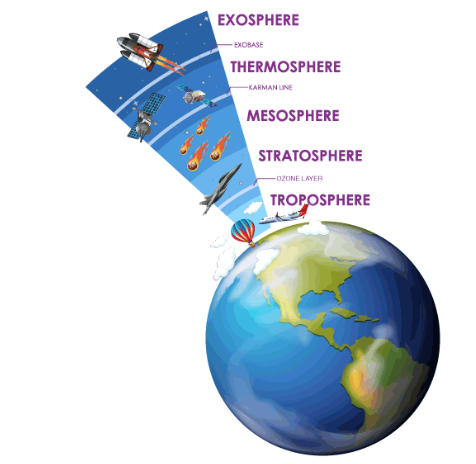
Classification of Atmospheric Layers:
- The atmosphere is divided into several layers based on temperature variations and composition:
- Troposphere: The lowest layer where weather occurs, and temperature decreases with altitude.
- Stratosphere: Above the troposphere, it contains the ozone layer and experiences a temperature increase with altitude.
- Mesosphere: The middle layer with a temperature decrease as altitude increases.
- Thermosphere: The outermost layer with high temperatures but low density. It includes the ionosphere.
- Exosphere: The boundary between Earth's atmosphere and outer space.
Functions and Importance:
- Supports Life: Provides the oxygen required for respiration and protects from harmful solar radiation.
- Regulates Climate: Influences temperature and weather patterns, helping maintain a stable environment.
- Aids in Navigation: Enables the use of instruments like GPS by allowing the propagation of radio waves.
- Protects from Space Debris: Shields Earth from meteoroids, which burn up in the atmosphere.
- Absorbs Solar Energy: The atmosphere absorbs and redistributes heat from the Sun, affecting climate.
Challenges:
- Air Pollution: The release of pollutants and greenhouse gases into the atmosphere can lead to environmental and health issues.
- Climate Change: Elevated levels of greenhouse gases are causing global warming and climate variability.
- Ozone Depletion: The depletion of the ozone layer in the stratosphere due to human-made chemicals poses risks to human health and the environment.
Understanding the Earth's atmosphere and its classification is crucial for climate science, meteorology, and environmental studies. It plays a significant role in shaping our planet's conditions and is central to many scientific and practical applications.
mportance of the Atmosphere
The atmosphere plays a crucial role in regulating Earth's climate and weather patterns. It helps to distribute heat around the planet, resulting in different climate zones and weather patterns. The atmosphere also acts as a protective shield, absorbing and scattering harmful solar radiation and preventing it from reaching the Earth's surface in excessive amounts.
Conclusion
The atmosphere is a layer of gas and suspended solids that surrounds the Earth. It is essential for supporting life, regulating climate, and protecting us from harmful radiation. The Earth's atmosphere is divided into several layers, each with its own unique characteristics. Understanding the atmosphere is crucial for studying weather, climate, and the overall dynamics of our planet.
Comment List
Leave a Comment.