Circuits
An introduction to Circuits
Name: Own Teacher
Email: info@ownteacher.com
Created At: 01-11-2023
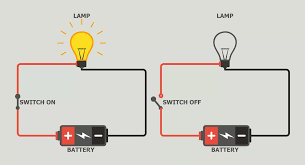
A circuit is a closed loop or pathway through which electric current flows, allowing the controlled transfer of electrical energy and information. Circuits are fundamental to electronics and electrical engineering, serving various purposes, from powering devices to processing signals. Here's a comprehensive explanation:
Components: Circuits consist of electrical components, including resistors, capacitors, inductors, diodes, transistors, and more. These components control and manipulate the flow of electrons.
Power Source: A circuit typically connects to a power source, like a battery or power supply. This source provides the voltage needed to drive the current through the circuit.
Wires or Conductors: Conductive materials, often copper or aluminum, connect the components, forming a closed loop. Wires act as pathways for the flow of electrons.
Current: Electric current is the movement of electrons through the circuit. It flows from the positive terminal of the power source to the negative terminal.
Voltage: Voltage, measured in volts, represents the electrical potential difference between two points in the circuit. It drives the flow of current.
Resistance: Resistance, measured in ohms, opposes the flow of current. It determines how much current can pass through a component. Ohm's Law (V = I * R) relates voltage, current, and resistance.
Series and Parallel Circuits: Circuits can be arranged in series, where components are connected end-to-end, or in parallel, where they have multiple pathways. Series circuits have the same current, while parallel circuits have the same voltage.
Digital and Analog Circuits: Circuits can be classified as digital or analog. Digital circuits process discrete binary signals (0s and 1s) used in computing, while analog circuits work with continuous signals like those in audio or video processing.
Integrated Circuits (ICs): ICs, or microchips, contain complex circuits with numerous components on a single semiconductor substrate. They are the building blocks of modern electronics.
Circuit Analysis: Engineers and technicians analyze circuits to understand their behavior, using tools like Kirchhoff's laws and circuit simulation software.
Circuit Diagrams: Schematic diagrams are used to represent circuits graphically. They use symbols to represent components and lines to indicate connections and flow of current.
Applications: Circuits are essential in countless applications, from simple household devices like light switches to complex systems like computers, communication networks, and control systems in manufacturing.
Troubleshooting: Troubleshooting circuits involves identifying and resolving issues, such as open circuits, short circuits, or faulty components.
In summary, circuits are the foundation of modern technology, enabling the control and utilization of electricity for various purposes. Understanding the principles of circuits is crucial for anyone involved in electronics, electrical engineering, or related fields.
Comment List
Leave a Comment.