Fluids
An introduction to Fluids
Name: Own Teacher
Email: info@ownteacher.com
Created At: 31-10-2023
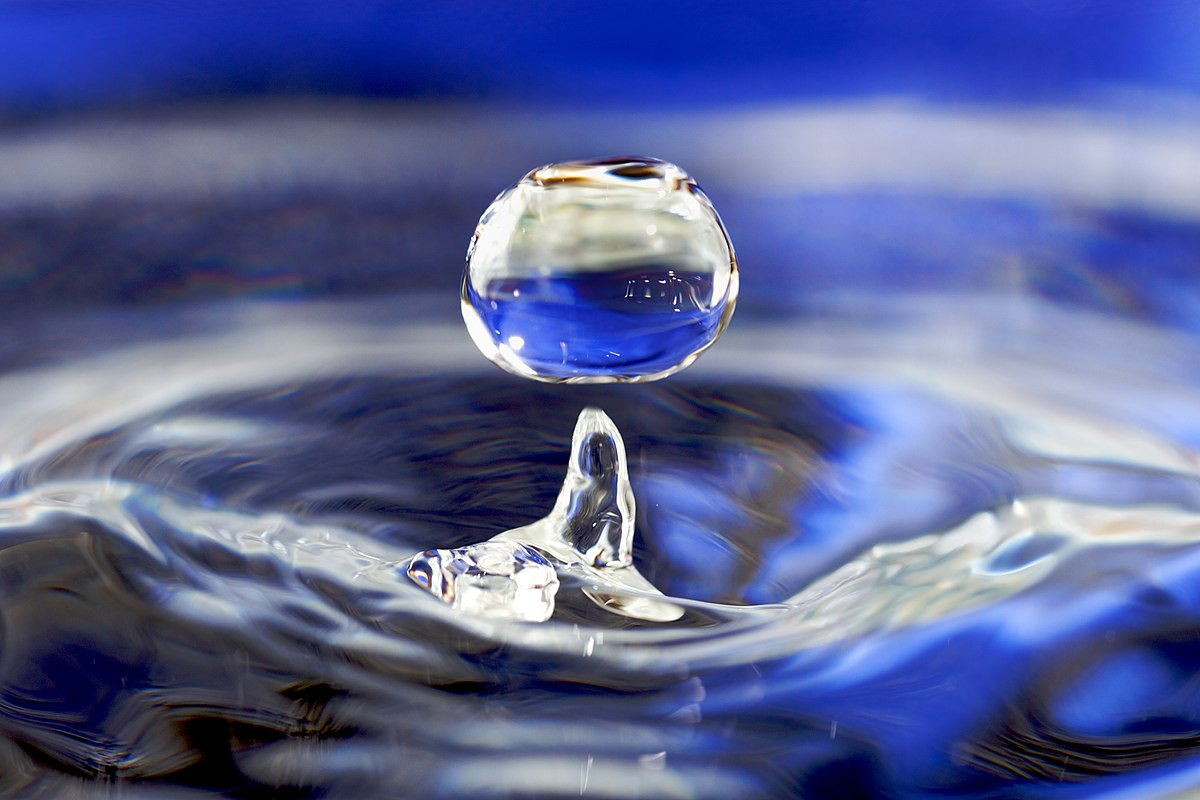
Fluids are substances that can flow and adapt to the shape of their container. They encompass both liquids (e.g., water, oil) and gases (e.g., air, hydrogen). Here's a comprehensive explanation:
1. Fluid Behavior:
- Fluids have the unique property of not maintaining a fixed shape and instead taking the shape of their container. They can flow and deform under the influence of external forces.
2. Viscosity:
- Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's resistance to flow. It is responsible for the "thickness" of a fluid. High-viscosity fluids flow more slowly than low-viscosity fluids.
3. Density:
- Density is the mass of a substance per unit volume. It defines how much matter is packed into a given space and influences buoyancy.
4. Buoyancy:
- Buoyancy is the upward force exerted on an object immersed in a fluid. It's related to the object's weight, volume, and the density of the fluid.
5. Fluid Dynamics:
- Fluid dynamics is the study of how fluids flow and behave. It includes the principles of fluid motion and is fundamental in understanding various applications.
6. Fluid Mechanics:
- Fluid mechanics is a branch of physics that deals with the behavior of fluids. It's important in engineering, environmental science, and many other fields.
7. Bernoulli's Principle:
- Bernoulli's principle states that as the speed of a fluid increases, its pressure decreases. It explains phenomena like lift in aviation.
8. Archimedes' Principle:
- Archimedes' principle states that an object immersed in a fluid experiences an upward buoyant force equal to the weight of the displaced fluid. It's crucial in understanding flotation.
9. Flow Behavior:
- Fluids can exhibit laminar flow (smooth, orderly) or turbulent flow (chaotic, irregular) depending on factors like velocity and viscosity.
10. Ideal and Real Fluids: - Ideal fluids follow idealized fluid dynamics laws with no viscosity, while real fluids exhibit viscosity and follow more complex behavior.
11. Applications: - Fluids are integral to numerous applications, including hydraulic systems, aviation, marine engineering, plumbing, HVAC systems, and chemical processing.
12. Environmental Relevance: - Fluid dynamics play a role in natural phenomena like weather patterns, ocean currents, and geological processes.
13. Ongoing Research: - Research in fluid dynamics and fluid mechanics continues to advance our understanding of these behaviors, leading to innovations in technology and science.
Fluids are a fundamental aspect of our physical world, and understanding their behavior is critical in a wide range of scientific, engineering, and practical applications.
Comment List
Leave a Comment.