Metabolism in Biology: The complete guide
AN INTRODUCTION TO Metabolism in Biology: The complete guide
Name: Own Teacher
Email: info@ownteacher.com
Created At: 06-11-2023
A comprehensive guide to metabolism in biology would be extensive, but I can provide a general overview:
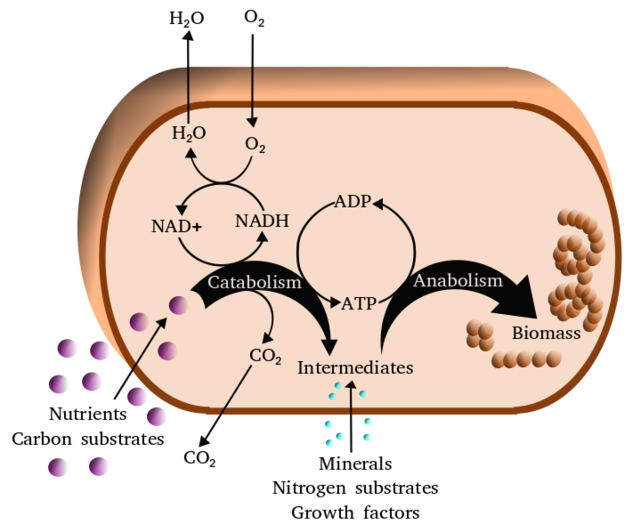
Metabolism is the sum of all chemical reactions that occur within an organism to maintain life. It can be divided into two main processes:
Anabolism: This involves the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler ones. Anabolic pathways require energy input and are responsible for processes like building proteins, nucleic acids, and cell structures.
Catabolism: This is the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones, releasing energy in the process. Catabolic pathways are responsible for processes like the breakdown of food molecules (carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) to generate energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
A comprehensive guide to metabolism in biology would be extensive, but I can provide a general overview:
Metabolism is the sum of all chemical reactions that occur within an organism to maintain life. It can be divided into two main processes:
Anabolism: This involves the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler ones. Anabolic pathways require energy input and are responsible for processes like building proteins, nucleic acids, and cell structures.
Catabolism: This is the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones, releasing energy in the process. Catabolic pathways are responsible for processes like the breakdown of food molecules (carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) to generate energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Key concepts in metabolism include:
- Enzymes: Biological catalysts that facilitate and speed up chemical reactions, playing a crucial role in metabolism.
- Energy production: Metabolism is central to energy production, where cells generate ATP through processes like glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
- Nutrient utilization: Metabolism governs the breakdown and utilization of nutrients such as glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids for energy and building blocks.
- Metabolic pathways: These are series of chemical reactions that occur in a coordinated manner to achieve specific metabolic goals, such as the breakdown of glucose through glycolysis.
- Metabolic regulation: The control of metabolic pathways through feedback mechanisms and hormonal signals to maintain a balance in the body's energy and nutrient needs.
- Metabolic disorders: Conditions like diabetes, obesity, and metabolic syndrome result from dysregulation in metabolic processes.
- Metabolic rate: It refers to the rate at which an organism expends energy, and it varies based on factors like age, genetics, and activity level.
- Hormones and metabolism: Hormones such as insulin and glucagon play a key role in regulating blood sugar levels and metabolism.
- Metabolic adaptation: The ability of the body to adjust its metabolic processes in response to changes in diet, physical activity, and other environmental factors.
- Metabolomics: The study of all the small molecules (metabolites) in a biological system to understand metabolic pathways and their regulation.
- Metabolic health: An overall measure of how well an organism's metabolism functions and its impact on health and disease.
Understanding metabolism is fundamental in biology, as it influences growth, energy balance, and overall health. This guide should serve as an introduction to the intricate world of biological metabolism, with in-depth exploration required for a complete understanding.
Comment List
Leave a Comment.