Oscillation
An introduction to Oscillation
Name: Own Teacher
Email: info@ownteacher.com
Created At: 31-10-2023
Oscillation
Oscillation refers to the action or state of oscillating, which involves variation, fluctuation, or a flow of electricity changing periodically from a maximum to a minimum . It is a common phenomenon observed in various fields, including physics, engineering, music, and climate science.
Types of Oscillation
There are different types of oscillation, each with its own characteristics and applications. Here are a few examples:
Coupled Oscillators: Coupled oscillators are a special case where energy alternates between two forms of oscillation. An example is the Wilberforce pendulum, where the oscillation alternates between the elongation of a vertical spring and the rotation of an object at the end of that spring .
Brain Oscillations: In neuroscience, brain oscillations refer to the rhythmic electrical activity in the brain. Different brain-wave types, such as alpha, beta, gamma, delta, and theta, signify different states of the brain .
Climate Oscillations: Climate oscillations, such as the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) and the Arctic Oscillation (AO), are large-scale patterns of climate variability. ENSO refers to the cycle of warm and cold ocean temperatures in the Pacific, which can influence weather patterns globally [3]. The AO is an atmospheric circulation pattern over the mid-to-high latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere.
Importance and Applications
Oscillation plays a crucial role in various fields and has practical applications. Here are a few examples:
Engineering and Control Theory: In process control and control theory, rapid oscillation may be an undesirable phenomenon. Techniques like sliding mode control are used to mitigate oscillations and stabilize systems.
Music: Oscillation is also relevant in the field of music. The Oscillation is a band known for their music, and they have released several albums and singles In music production, oscillators are used to generate sound waves and create different tones and effects.
Climate and Weather: Climate oscillations, such as ENSO and AO, have significant impacts on weather patterns and climate variability. Understanding these oscillations helps in predicting and studying climate phenomena, such as extreme weather events and long-term climate trends.
Conclusion
Oscillation is a fundamental concept that describes the action or state of oscillating. It is observed in various fields, including physics, engineering, music, and climate science. Different types of oscillation have specific characteristics and applications. Understanding and studying oscillations are crucial for advancing knowledge and developing practical solutions in these fields.
Harmonic Oscillation
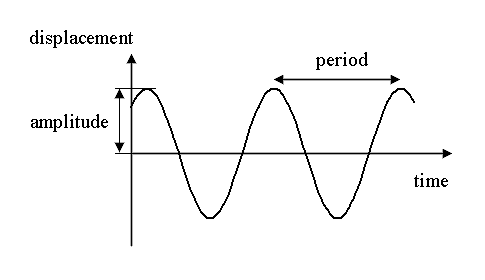
Harmonic oscillation, also known as simple harmonic motion (SHM), is a type of periodic motion in which an object oscillates back and forth around an equilibrium position under the influence of a restoring force. The motion is characterized by a sinusoidal pattern with a constant amplitude and a specific frequency or period.
Characteristics of Harmonic Oscillation
The motion of a harmonic oscillator can be described by several key characteristics:
Amplitude: The amplitude of a harmonic oscillator represents the maximum displacement of the object from its equilibrium position. It determines the range of motion of the oscillator.
Period and Frequency: The period of a harmonic oscillator is the time taken to complete one full oscillation, while the frequency is the number of oscillations per unit time. The period and frequency are inversely related and depend on the mass of the object and the force constant of the restoring force.
Phase: The phase of a harmonic oscillator determines the starting point on the sinusoidal wave. It represents the position of the object at a given time within the oscillation cycle.
Velocity and Acceleration: The velocity and acceleration of a harmonic oscillator also exhibit oscillatory behavior with the same frequency as the position but with shifted phases. The velocity is maximum when the displacement is zero, while the acceleration is in the opposite direction to the displacement.
Mathematical Representation
The position of a harmonic oscillator as a function of time can be described by a sinusoidal equation. For example, the position of an object undergoing harmonic oscillation can be represented as:
x(t) = A * sin(ωt + φ)
where:
- x(t) is the position of the object at time t
- A is the amplitude of the oscillation
- ω is the angular frequency (related to the period and frequency)
- φ is the phase of the oscillation.
Applications of Harmonic Oscillation
Harmonic oscillation has various applications in different fields:
Physics: Harmonic oscillators serve as important models in physics, providing insights into the behavior of systems under the influence of restoring forces. They are used to study phenomena such as mass-spring systems, pendulums, and vibrating strings.
Engineering: Understanding harmonic oscillation is crucial in engineering disciplines. It helps in designing and analyzing systems involving vibrations, such as mechanical structures, electrical circuits, and control systems.
Music: Harmonic oscillation is fundamental to the production of sound in musical instruments. Vibrating strings, air columns in wind instruments, and oscillating membranes in drums all rely on harmonic oscillation to create specific tones and harmonics.
Quantum Mechanics: Harmonic oscillators play a significant role in quantum mechanics. They serve as a basis for understanding the behavior of quantum systems, such as the quantization of energy levels and the concept of zero-point energy.
Conclusion
Harmonic oscillation, or simple harmonic motion, is a type of periodic motion characterized by a sinusoidal pattern with a constant amplitude and frequency. It is a fundamental concept in physics, engineering, music, and quantum mechanics. Understanding harmonic oscillation helps in analyzing and predicting the behavior of systems under the influence of restoring forces.
Comment List
Leave a Comment.