The law of conservation of linear momentum
An introduction to The law of conservation of linear momentum
Name: Own Teacher
Email: info@ownteacher.com
Created At: 28-10-2023
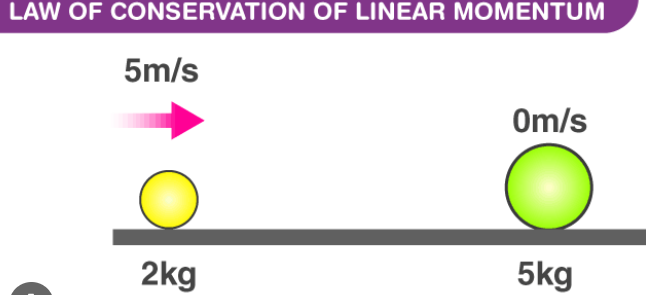
The law of conservation of linear momentum, often referred to as the conservation of momentum, is a fundamental principle in physics. It states that the total linear momentum of an isolated system remains constant over time, provided that no external forces act on the system. In other words, the momentum of a closed system is conserved.
Here's a more detailed explanation of this law:
Linear Momentum: Linear momentum (p) is a vector quantity that represents the motion of an object. It is defined as the product of an object's mass (m) and its velocity (v), mathematically expressed as: p = mv
The direction of the momentum is the same as the direction of the velocity.
Conservation Law: A conservation law in physics is a principle that states that a certain quantity remains constant within an isolated system. In the case of the law of conservation of linear momentum, it means that the total linear momentum of an isolated system remains constant as long as there are no external forces acting on the system.
Isolated System: An isolated system is one that does not exchange matter or energy with its surroundings. In the context of momentum conservation, this means that the system is not influenced by any external forces or interactions from outside the system.
Application of the Law: When two or more objects interact within a closed system, their individual momenta can change. However, the law of conservation of linear momentum ensures that the total momentum of the system before the interaction is equal to the total momentum after the interaction. This is true for both elastic and inelastic collisions, as long as no external forces are involved.
Mathematical Representation: Mathematically, the law of conservation of linear momentum can be expressed as follows: Σp_initial = Σp_final
Here, Σp_initial represents the total initial momentum of all objects in the system, and Σp_final represents the total final momentum of the same objects after the interaction.
Real-World Examples: This law has practical applications in various aspects of physics and engineering, including understanding the motion of celestial bodies, analyzing the behavior of particles in particle accelerators, and designing vehicle safety systems, such as airbags, that rely on the principles of momentum conservation to protect occupants during collisions.
In summary, the law of conservation of linear momentum is a fundamental principle in physics that states that within an isolated system, the total momentum remains constant unless acted upon by external forces. This law plays a crucial role in understanding and predicting the behavior of objects in motion, making it an essential concept in classical mechanics.
Comment List
Leave a Comment.