waves
An introduction to waves
Name: Own Teacher
Email: info@ownteacher.com
Created At: 31-10-2023
Waves are a fundamental concept in physics and the natural world, representing the transfer of energy from one place to another without a net movement of matter. Waves can take various forms and occur in many contexts, including mechanical waves, electromagnetic waves, and more. Here is a full explanation of waves:
Definition: A wave is a disturbance or oscillation that propagates through space or a medium, carrying energy with it. Waves can be characterized by their properties, such as amplitude, frequency, wavelength, and speed.
Key Characteristics of Waves:
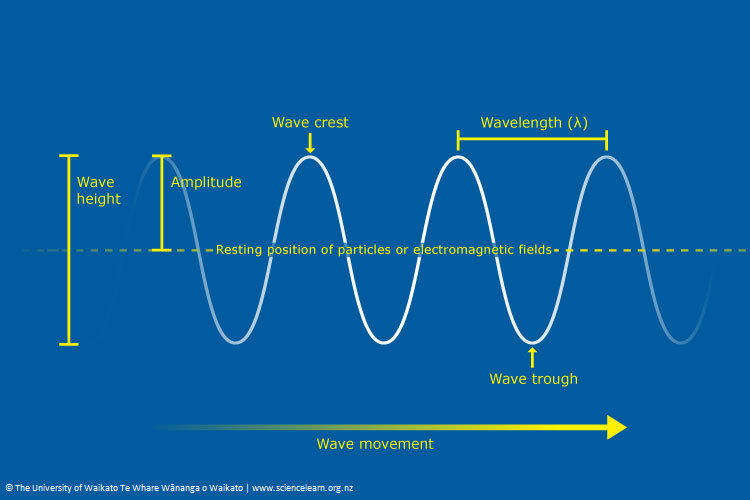
Amplitude: The amplitude of a wave is the maximum displacement from the equilibrium position. In the case of a transverse wave (like a water wave or light wave), this is the maximum height or distance from the baseline. In longitudinal waves (like sound waves), it represents the maximum compression or rarefaction.
Frequency: Frequency (f) is the number of oscillations or cycles of a wave that occur per unit time. It's measured in hertz (Hz), with one hertz representing one cycle per second.
Wavelength: Wavelength (λ) is the distance between two consecutive points in a wave that are in phase, such as two wave crests or troughs. It's typically measured in meters.
Propagation: Waves can be classified based on how they propagate. Transverse waves have oscillations perpendicular to the direction of propagation, while longitudinal waves have oscillations parallel to the direction of propagation.
Wave Speed: The speed of a wave (v) is the rate at which it travels through a medium. It's determined by the medium's properties and the wave's frequency and wavelength. The formula is v = f * λ.
Types of Waves:
Mechanical Waves: These waves require a material medium for propagation. Examples include water waves, sound waves, and seismic waves.
Electromagnetic Waves: These waves do not require a medium and can travel through a vacuum. They include visible light, radio waves, microwaves, and X-rays.
Wave Behavior:
Reflection: Waves bounce back when they encounter a barrier or a different medium, following the law of reflection.
Refraction: Waves change direction as they pass from one medium to another with a different wave speed, following the law of refraction.
Interference: When two or more waves meet, they can combine to create a new wave with a different amplitude, known as interference.
Diffraction: Waves bend around obstacles or spread out when passing through narrow openings, known as diffraction.
Polarization: Some waves exhibit polarization, where their oscillations occur in a specific direction, making them useful for applications like 3D glasses and polarized sunglasses.
Applications:
Sound Waves: Used in communication, music, and medical imaging like ultrasound.
Light Waves: Essential for vision, telecommunications, and various technologies, including lasers and fiber optics.
Radio Waves: Used in broadcasting, wireless communication, and radar systems.
Microwaves: Used in microwave ovens, satellite communication, and radar.
Water Waves: Important in understanding oceanography and coastal processes.
Seismic Waves: Help in studying Earth's interior, detecting earthquakes, and exploring for natural resources.
Electromagnetic Waves: Play a fundamental role in astronomy, remote sensing, and medical imaging.
Waves are a central concept in physics and have a wide range of applications in science, technology, and everyday life. They are essential for understanding how energy and information travel through our world.
Comment List
Leave a Comment.